AI Agent Market Landscape: Hype Ends, Technology Continues
Author: Tiger Research
Translation: AididiaoJP, Foresight News
Summary
- The AI agent market cooled off rapidly after token prices plummeted, but technical development continues steadily. The DeFAI sector has regained attention through actual product launches and professional on-chain functionalities.
- Specialized agents optimized for specific functions have replaced previous general-purpose agents. Projects like Virtuals are actively building infrastructure to connect these agents and enable collaboration.
- AI agents will be integrated as core functionalities in crypto projects. Infrastructure that enables smooth communication and collaboration between agents will become crucial.
The Hype Ends, Technology Continues
The crypto industry has integrated AI technology in various ways, with AI agents receiving the most attention. The total market cap of tokens related to agents once reached about 16 billions USD. This demonstrated strong market interest, but the attention was short-lived. Most projects failed to meet development expectations, and token prices plummeted by more than 90% from their peaks.
The price drop does not represent a technological setback. AI agents remain an important technical field within crypto. Discussions about actual use cases have become more specific, and teams continue to test new approaches. This report explores how AI agents function within the crypto space and examines potential future developments.
Reshaping the AI Agent Ecosystem After the Hype
Early AI Agent Projects Gradually Fade from the Market
The AI agent sector within crypto began attracting attention at the end of 2024. The ElizaOS from the ai16z team and the G.A.M.E development stack from the Virtuals Protocol team significantly lowered the threshold for agent development. Launch platforms like DAOS.fun and Virtuals Fun provided platforms for tokenizing developed agents. The process from development to launch became simplified, market interest exploded, and a large number of agent projects emerged rapidly.
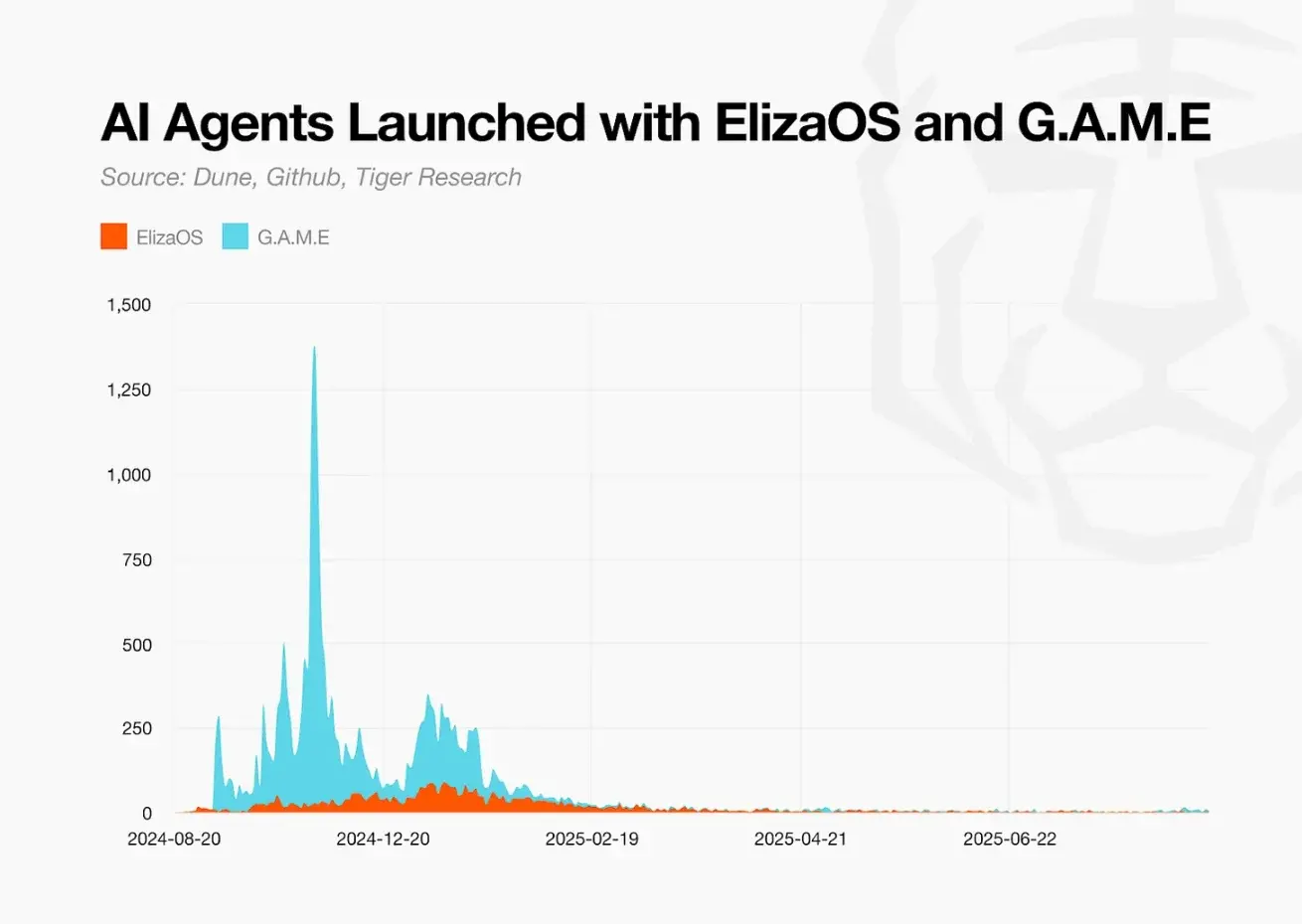
Most projects proposed ambitious roadmaps leveraging AI technology. Investors drove up token prices in anticipation of innovative services. In reality, these projects were merely wrappers for fine-tuned or prompt-engineered OpenAI or Anthropic base models. Most projects built advanced chatbots for X or Telegram, rather than developing independent services. Projects emphasized innovative vision and technological differentiation, but their actual operations were almost indistinguishable from meme coins.

However, there were some exceptions. Projects like aixbt and Soleng partially delivered on their roadmaps and launched actual services. They adopted token gating to provide exclusive access for token holders. Aixbt offers project analysis reports, while Soleng analyzes Github code repositories to support investor decision-making.
Even these relatively successful cases could not overcome structural limitations. The unstable revenue model relying solely on rising token prices hindered progress. Their technological competitiveness lagged behind Web2 companies. Token prices eventually fell, operational funds dried up, and most projects have now suspended services.
DeFAI Projects Rekindle Hope in the Sector
AI agent technology once faced excessive expectations and has now entered a correction phase. The DeFAI sector has regained attention by proving its actual value. DeFAI agents execute automated investment strategies 24/7. They enable users to easily access complex DeFi services through simple natural language commands. This sector was the core narrative of the early AI agent space. Most projects remained at the roadmap stage and struggled to implement in practice. The sector temporarily lost attention. Recent product launches are rebuilding market expectations.
Representative projects include Wayfinder and HeyAnon. Wayfinder executes on-chain tasks through dedicated AI agents called "Shells." Shells execute on-chain transactions directly via built-in dedicated wallets. The system adopts a specialized multi-agent architecture, including trading agents, perpetual agents, and contract agents. Each agent type focuses on a specific role to automate various investment strategies. Users can easily execute simple cross-chain trades or advanced strategies such as basis trading and leveraged dollar-cost averaging.
From Individual Agents to Agent Networks
Early AI agent projects promoted "general-purpose agents" that performed all functions. This approach prioritized fundraising over technical completeness. Projects proposed excessive roadmaps to capture a broader market. Most exposed their limitations during the implementation phase.
The current agent ecosystem is evolving in a completely different direction. Builders have recognized the limitations of general-purpose agents and are now developing agents focused on specific domains. These agents can collaborate with each other, similar to skilled craftsmen—carpenters, electricians, plumbers, etc.—with different expertise working together to build a house.
Virtuals Protocol's ACP represents this trend. It provides a standard framework for communication and task allocation between different agents. Theoriq and General Impression are also building infrastructure to enhance interoperability between agents. The market is being reshaped, shifting toward maximizing the value of the entire agent ecosystem rather than individual agents.
Future Scenarios for the AI Agent Market
After the early hype cooled, AI agents continue to evolve. Speculation has ended, but projects continue to leverage AI agents to build new functionalities and services. Two changes stand out in particular.
First, AI agents are becoming essential infrastructure. AI agents are no longer a standalone field but are being integrated as basic functionalities within crypto projects. Blockchain data platform Nansen is developing research agents to make complex on-chain data easier to explore. DeFi projects are also adding agents to improve user access. AI agents will become the final interface connecting users with the blockchain, rather than an optional feature.
Second, agent commerce will grow. As AI agents become standard, interactions between agents and between agents and humans will become more frequent. Secure transaction protocols and trust mechanisms are becoming increasingly important. Projects like Virtuals Protocol's ACP are laying the foundation for this.
These changes will simplify the complexity of the crypto space, improve user experience, and create new economic opportunities.