Top AI models diverge: GPT to C, Claude to B
According to the Anthropic Economic Index Report, 77% of Claude users focus on business applications, and 36% specifically use it for programming tasks, demonstrating a clear enterprise-level characteristic. In contrast, OpenAI research shows that 73% of ChatGPT usage is unrelated to work, with the tool serving more as a personal assistant.
Written by: Dong Jing
Source: Wallstreetcn
The global AI market is showing a clear trend of user group differentiation. Latest data from OpenAI and Anthropic, two major giants, indicate that ChatGPT is becoming the preferred personal life assistant, while Claude is taking a dominant position in enterprise automation deployment.
According to previous news from Chasing Wind Trading Desk, Barclays stated in its latest research report that data shows Anthropic's API business accounts for as much as 90% of its revenue, far exceeding OpenAI's 26%, highlighting Claude's strong position in the B-end (enterprise) market.
User behavior analysis further confirms this trend of differentiation. According to the Anthropic Economic Index Report, 77% of Claude users focus on business applications, and 36% specifically use it for programming tasks, demonstrating a clear enterprise-level characteristic. In contrast, OpenAI research shows that 73% of ChatGPT usage is unrelated to work, with the tool serving more as a personal assistant.
Analysis points out that the world's two top AI models are showing distinctly different business paths: Claude, with its advantages in API integration and enterprise automation, is reshaping the landscape of B-end AI services, while ChatGPT continues to consolidate its leadership in the consumer market.
Claude Establishes Leading Advantage in API Market
According to Chasing Wind Trading Desk, Barclays previously stated that Anthropic has built significant competitive barriers in the enterprise-level AI service market.
Data shows that 90% of Anthropic's revenue comes from API business, while only 26% of OpenAI's revenue is derived from this channel, with its main revenue still relying on ChatGPT consumer products.
Revenue growth data further highlights Claude's strong momentum in the B-end market.
Anthropic's API business achieved $512 million in revenue in 2024, and is expected to surge to $3.907 billion in 2025, a year-on-year increase of 662%. In contrast, OpenAI's API business revenue is $1 billion in 2024, expected to grow to $1.8 billion in 2025, an increase of 80%.
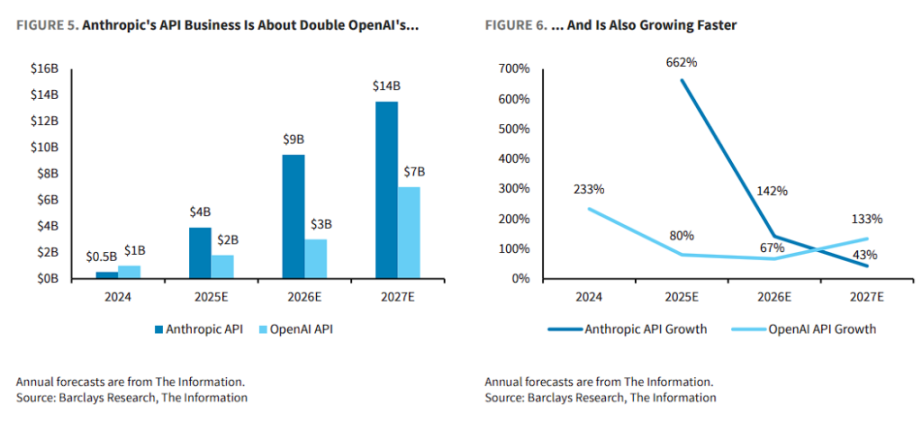
Analysis points out that this difference in revenue structure reflects the different strategic focuses of the two companies. Claude focuses on providing programmable integrated AI capabilities for enterprise clients, while ChatGPT relies more on a subscription-based consumer service model.
Usage Scenario Differentiation Confirms Commercial Positioning Differences
User behavior data further confirms the different positioning of the two major AI models.
According to the Anthropic Economic Index Report, Claude users show obvious commercial characteristics: 77% of usage scenarios involve business applications, and 36% are specifically for programming tasks.
Among API clients, this trend is even more pronounced, with 77% of enterprise usage showing an automation model, mainly for task delegation rather than collaborative interaction.
OpenAI's research paints a completely different picture.
Analysis based on 1.5 million user chat records shows that non-work usage has become the main application scenario for ChatGPT. In June 2024, work and personal use were roughly equal, but by June 2025, non-work usage accounted for 73% of all conversations.
In the classification of over 1 million conversations, "practical guidance" accounted for 28.3%, covering personal needs such as daily advice, academic help, and fitness guidance, with writing assistance ranking second.
The difference in the frequency of programming tasks is also quite telling. Among Claude users, 36% are engaged in programming-related work, while only 4.2% of ChatGPT user conversations involve programming, further highlighting the differentiation in target user groups.
Enterprise Automation Demand Drives Claude's Growth
Claude's success in the enterprise market stems from its precise grasp of automation needs.
API data shows that enterprise clients mainly use Claude for programmable integrated task execution, rather than collaborative human-computer interaction. This usage pattern is highly consistent with enterprises' pursuit of efficiency and scalability.
In terms of task distribution, Claude's API clients concentrate 44% of usage on computer and mathematics tasks, much higher than the 36% on the Claude.ai platform. At the same time, office and administrative management tasks account for about 10%, reflecting the strong demand for automated office tasks. Enterprises also deploy Claude in areas such as marketing material creation and business recruitment data processing.
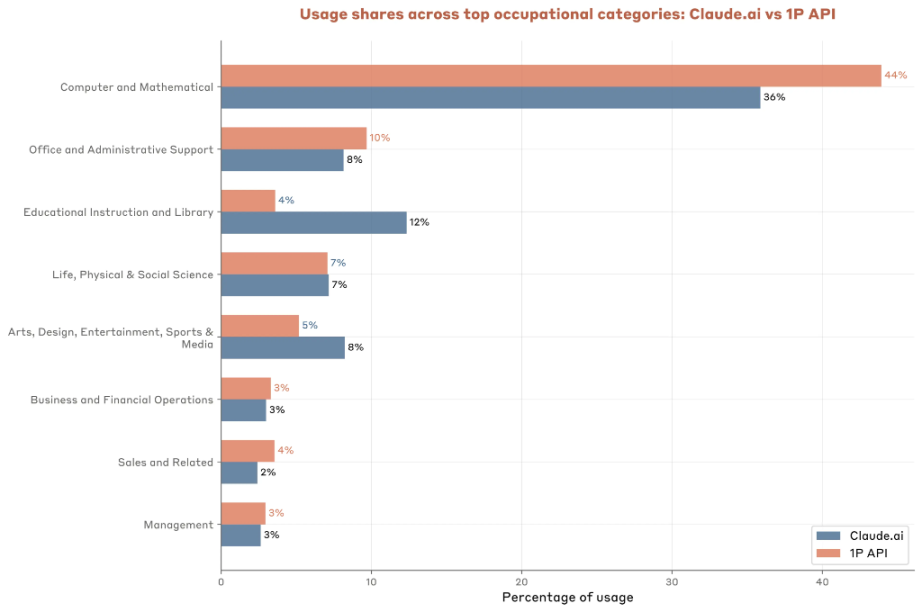
Surprisingly, enterprises are relatively insensitive to the cost of AI usage.
For every 1% increase in cost, usage frequency decreases by only 0.29%, indicating that model capability, deployment ease, and economic value are more important than cost. More expensive tasks often have higher usage rates; computer and mathematics tasks cost more than 50% higher than sales-related tasks, but dominate in usage volume.
Geographical Distribution Reflects Different Market Strategies
The geographical usage patterns of the two major AI models also reflect different market positioning.
Claude's usage rate is strongly positively correlated with national GDP; for every 1% increase in per capita GDP, Claude's usage rate increases by 0.7%. Technologically advanced small economies such as Israel and Singapore lead the world in Claude adoption rates.
In the US market, Washington D.C. and Utah lead in per capita Claude usage, reflecting the high demand for enterprise-level AI tools in government departments and the technology industry. This distribution pattern aligns with Claude's positioning towards high-value enterprise clients.
ChatGPT, on the other hand, shows a broader trend of global adoption.
OpenAI research shows that ChatGPT's growth rate in poorer countries exceeds that in wealthy countries, and its user base is more diverse. As of June 2025, 52% of ChatGPT users are female, and nearly half are aged between 18 and 25.
Technical Capability Differentiation Shapes Competitive Landscape
The different technical focuses of Claude and ChatGPT are shaping their respective competitive advantages.
Claude excels in code generation, debugging, and technical problem-solving, which is closely related to its success in the API market.
The rapid adoption of new tools by the developer community and the relatively low organizational barriers for individual developers have laid the foundation for Claude's enterprise-level applications.
ChatGPT, on the other hand, has greater advantages in information retrieval and personal guidance.
"Information search" has become the third largest usage scenario for ChatGPT, with users seeing it as an alternative to web search. Analysis suggests that this application model poses a potential challenge to traditional search engines such as Google, and also creates opportunities for OpenAI to explore new revenue sources such as advertising and e-commerce recommendations.
The differences between Claude and ChatGPT in human-computer collaboration models are also noteworthy.
Claude users are more inclined to delegate complete tasks to AI for execution, reflecting enterprises' preference for automation. ChatGPT users, on the other hand, are more likely to adopt collaborative interactions, which aligns with the learning and exploration needs of individual users.